Accelerated modern human–induced species losses: Entering the sixth mass extinction
Accelerated modern human–induced species losses: Entering the sixth mass extinction
Abstract
The oft-repeated claim that Earth’s biota is entering a sixth “mass extinction” depends on clearly demonstrating that current extinction rates are far above the “background” rates prevailing between the five previous mass extinctions. Earlier estimates of extinction rates have been criticized for using assumptions that might overestimate the severity of the extinction crisis. We assess, using extremely conservative assumptions, whether human activities are causing a mass extinction.
First, we use a recent estimate of a background rate of 2 mammal extinctions per 10,000 species per 100 years (that is, 2 E/MSY), which is twice as high as widely used previous estimates. We then compare this rate with the current rate of mammal and vertebrate extinctions. The latter is conservatively low because listing a species as extinct requires meeting stringent criteria.
Even under our assumptions, which would tend to minimize evidence of an incipient mass extinction, the average rate of vertebrate species loss over the last century is up to 100 times higher than the background rate. Under the 2 E/MSY background rate, the number of species that have gone extinct in the last century would have taken, depending on the vertebrate taxon, between 800 and 10,000 years to disappear.
These estimates reveal an exceptionally rapid loss of biodiversity over the last few centuries, indicating that a sixth mass extinction is already under way. Averting a dramatic decay of biodiversity and the subsequent loss of ecosystem services is still possible through intensified conservation efforts, but that window of opportunity is rapidly closing.
 Fig. 1
Fig. 1
Cumulative vertebrate species recorded as extinct or extinct in the wild by the IUCN (2012).
Graphs show the percentage of the number of species evaluated among mammals (5513; 100% of those described), birds (10,425; 100%), reptiles (4414; 44%), amphibians (6414; 88%), fishes (12,457; 38%), and all vertebrates combined (39,223; 59%). Dashed black curve represents the number of extinctions expected under a constant standard background rate of 2 E/MSY. (A) Highly conservative estimate. (B) Conservative estimate.
The article should be considered in light of this estimate:
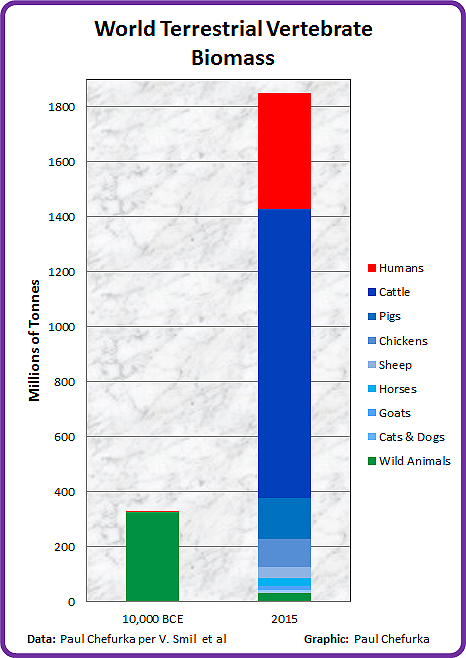
The decimation of wild animal biomass shown in my graphic reflects the extinctions analyzed by the authors of the Science article.

